 English
English Esperanto
Esperanto  Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Català
Català  שפה עברית
שפה עברית  Cymraeg
Cymraeg  Galego
Galego  Latviešu
Latviešu  icelandic
icelandic  ייִדיש
ייִדיש  беларускі
беларускі  Hrvatski
Hrvatski  Kreyòl ayisyen
Kreyòl ayisyen  Shqiptar
Shqiptar  Malti
Malti  lugha ya Kiswahili
lugha ya Kiswahili  አማርኛ
አማርኛ  Bosanski
Bosanski  Frysk
Frysk  ភាសាខ្មែរ
ភាសាខ្មែរ  ქართული
ქართული  ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી  Hausa
Hausa  Кыргыз тили
Кыргыз тили  ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ  Corsa
Corsa  Kurdî
Kurdî  മലയാളം
മലയാളം  Maori
Maori  Монгол хэл
Монгол хэл  Hmong
Hmong  IsiXhosa
IsiXhosa  Zulu
Zulu  Punjabi
Punjabi  پښتو
پښتو  Chichewa
Chichewa  Samoa
Samoa  Sesotho
Sesotho  සිංහල
සිංහල  Gàidhlig
Gàidhlig  Cebuano
Cebuano  Somali
Somali  Тоҷикӣ
Тоҷикӣ  O'zbek
O'zbek  Hawaiian
Hawaiian  سنڌي
سنڌي  Shinra
Shinra  Հայերեն
Հայերեն  Igbo
Igbo  Sundanese
Sundanese  Lëtzebuergesch
Lëtzebuergesch  Malagasy
Malagasy  Yoruba
Yoruba  অসমীয়া
অসমীয়া  ଓଡିଆ
ଓଡିଆ  Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик
How Can VOC Treatment Equipment Improve Industrial Air Quality?
2025-12-30
Abstract: VOC Treatment Equipment plays a pivotal role in industrial air quality management by controlling volatile organic compound emissions. This article provides a comprehensive overview of VOC treatment solutions, explores key operational parameters, examines common industry challenges, and addresses frequently asked questions. By understanding the mechanisms, applications, and maintenance of VOC Treatment Equipment, industries can enhance environmental compliance and ensure workplace safety.
Table of Contents
Introduction to VOC Treatment Equipment
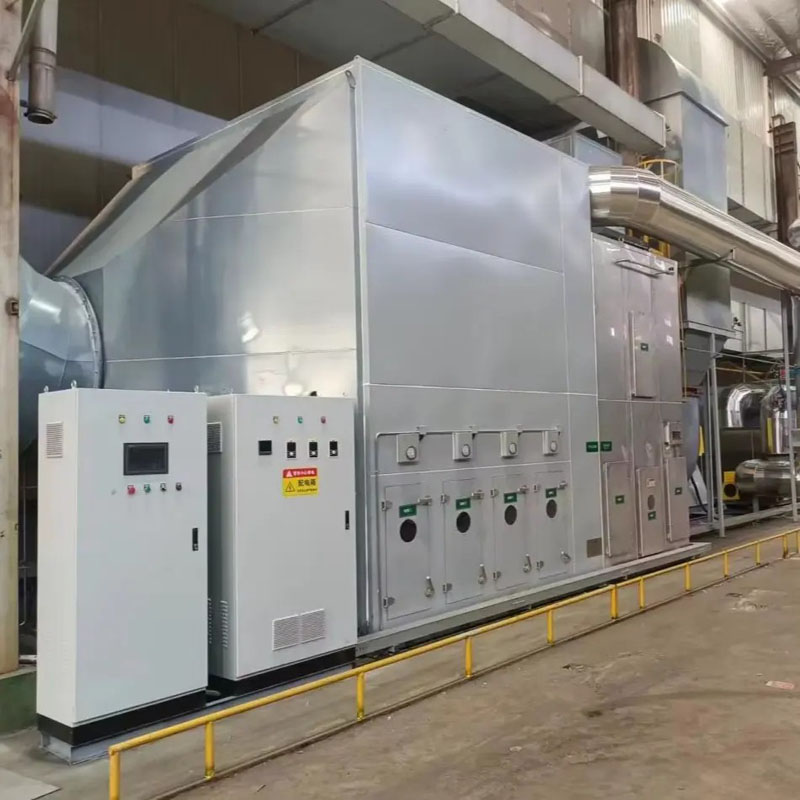
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) are a major contributor to industrial air pollution, originating from processes such as painting, coating, chemical manufacturing, and solvent handling. Effective VOC treatment is critical to meet environmental regulations, reduce workplace hazards, and minimize ecological impact. VOC Treatment Equipment refers to specialized machinery designed to capture, neutralize, or destroy VOC emissions through physical, chemical, or biological methods.
This article focuses on the core aspects of VOC Treatment Equipment, including performance parameters, operational principles, and common industry questions, aiming to guide companies in selecting and maintaining suitable solutions.
Key Technical Parameters of VOC Treatment Equipment
| Parameter | Typical Range/Specification | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Air Flow Rate | 500–5000 m³/h | Volume of air processed per hour, impacting overall VOC removal efficiency |
| VOC Removal Efficiency | 85–99% | Percentage of VOCs removed from exhaust air |
| Operating Temperature | 25–800°C | Depends on treatment method: adsorption, thermal oxidation, or bio-filtration |
| Pressure Drop | 50–200 Pa | Resistance generated by the equipment, affecting energy consumption |
| Power Consumption | 1–15 kW | Energy required to operate the equipment under standard conditions |
Types and Mechanisms of VOC Treatment Equipment
1. Adsorption Systems
Adsorption systems utilize activated carbon or other porous materials to trap VOC molecules from industrial exhaust streams. These systems are highly effective for low-concentration VOC emissions and are suitable for continuous operations.
2. Thermal Oxidizers
Thermal oxidizers use high temperatures to combust VOCs into carbon dioxide and water. They are appropriate for industries with high VOC concentrations and ensure rapid removal but require significant energy input.
3. Bio-Filtration Units
Bio-filters employ microorganisms to biodegrade VOCs into harmless by-products. These systems are energy-efficient, environmentally friendly, and ideal for moderate VOC loads with minimal hazardous by-products.
4. Catalytic Oxidation Systems
These systems accelerate VOC oxidation at lower temperatures using catalysts, providing energy savings while maintaining high efficiency. They are particularly suited for solvent recovery applications.
5. Wet Scrubbers
Wet scrubbers remove VOCs by contacting polluted air with a liquid absorbent. This method is effective for soluble VOCs and can be integrated with chemical neutralization for specific compounds.
Frequently Asked Questions About VOC Treatment Equipment
Q1: How to select the right VOC Treatment Equipment for a specific industry?
A1: Selection depends on VOC concentration, airflow volume, emission patterns, regulatory requirements, and operational costs. Adsorption systems are suitable for low-concentration VOCs, thermal oxidizers for high concentrations, and bio-filters for biodegradable VOCs. A thorough site assessment and pilot testing ensure optimal performance.
Q2: How to maintain VOC Treatment Equipment to ensure long-term efficiency?
A2: Maintenance involves regular inspection of filters, activated carbon replacement, catalyst monitoring, temperature control checks, and cleaning of bio-filtration media. Scheduled preventive maintenance reduces downtime, ensures consistent removal efficiency, and prolongs equipment lifespan.
Q3: How to measure the effectiveness of VOC Treatment Equipment?
A3: Effectiveness is measured using VOC concentration analysis before and after treatment. Gas chromatography or photoionization detectors are common methods. Monitoring parameters like airflow, temperature, and pressure drop also indicate operational efficiency.
Q4: How to handle fluctuations in VOC load and composition?
A4: Advanced VOC Treatment Equipment often includes modular systems, adjustable airflow, and variable thermal/catalytic control. Real-time monitoring and adaptive control systems allow the equipment to respond efficiently to changing emission conditions.
Q5: How to ensure compliance with local environmental regulations?
A5: Compliance requires understanding local emission limits, selecting equipment certified by recognized authorities, maintaining records of VOC removal efficiency, and periodic third-party audits. Proper equipment sizing and continuous monitoring are critical for regulatory adherence.
Conclusion and Contact
VOC Treatment Equipment remains an essential component in industrial air pollution control, providing reliable solutions to reduce volatile organic compound emissions. By selecting appropriate technologies, monitoring operational parameters, and implementing effective maintenance strategies, industries can achieve both regulatory compliance and environmental sustainability. Lano Machinery offers a wide range of VOC Treatment Equipment tailored for diverse industrial applications, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency.
For detailed inquiries, consultation, and personalized solutions, contact us today to learn how Lano Machinery can support your VOC management strategy.





