English
English Esperanto
Esperanto  Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Català
Català  שפה עברית
שפה עברית  Cymraeg
Cymraeg  Galego
Galego  Latviešu
Latviešu  icelandic
icelandic  ייִדיש
ייִדיש  беларускі
беларускі  Hrvatski
Hrvatski  Kreyòl ayisyen
Kreyòl ayisyen  Shqiptar
Shqiptar  Malti
Malti  lugha ya Kiswahili
lugha ya Kiswahili  አማርኛ
አማርኛ  Bosanski
Bosanski  Frysk
Frysk  ភាសាខ្មែរ
ភាសាខ្មែរ  ქართული
ქართული  ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી  Hausa
Hausa  Кыргыз тили
Кыргыз тили  ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ  Corsa
Corsa  Kurdî
Kurdî  മലയാളം
മലയാളം  Maori
Maori  Монгол хэл
Монгол хэл  Hmong
Hmong  IsiXhosa
IsiXhosa  Zulu
Zulu  Punjabi
Punjabi  پښتو
پښتو  Chichewa
Chichewa  Samoa
Samoa  Sesotho
Sesotho  සිංහල
සිංහල  Gàidhlig
Gàidhlig  Cebuano
Cebuano  Somali
Somali  Тоҷикӣ
Тоҷикӣ  O'zbek
O'zbek  Hawaiian
Hawaiian  سنڌي
سنڌي  Shinra
Shinra  Հայերեն
Հայերեն  Igbo
Igbo  Sundanese
Sundanese  Lëtzebuergesch
Lëtzebuergesch  Malagasy
Malagasy  Yoruba
Yoruba  অসমীয়া
অসমীয়া  ଓଡିଆ
ଓଡିଆ  Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик
Why Use Coking Equipment?
-
Why Use Coking Equipment?
-
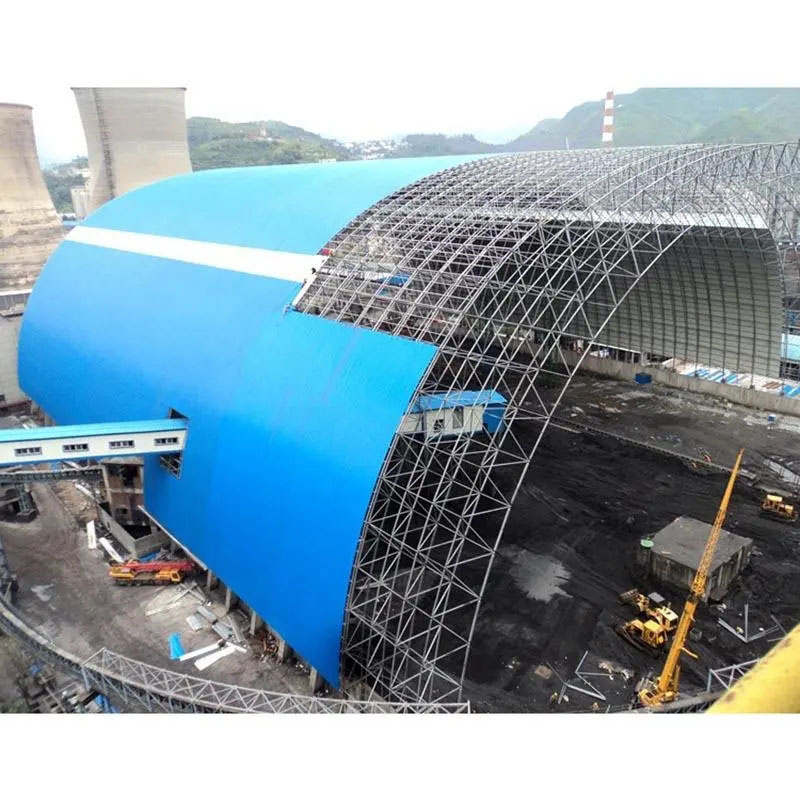
Deep Dive: Coke Guide & Coal Bunker
-
Technical Specifications of Our Coking Equipment
-
Common Questions & Answers about Coking Equipment
-
Recent Industry News & Summary / Contact
How does coking equipment work?
Coking equipment is designed to carry out coal carbonization (coking) — i.e. heating coal in an oxygen-deficient environment to drive off volatile compounds, leaving solid coke. This process typically involves: preheating, pyrolysis, gas release, controlled cooling, and handling of by-products such as coal gas and tars. The coking equipment provides the mechanical structure, heat management, sealing systems, and material handling required for safe, efficient, and continuous operation.
Why is coking equipment critical in industrial operations?
-
Efficiency & yield control: The right design allows optimization of coke yield and gas/volatile recovery.
-
Process stability & safety: Proper sealing, insulation, and control systems reduce heat loss, manage pressure, and maintain safe operation.
-
Emission control & environmental compliance: Modern coking equipment integrates gas capture, sulfur removal, and dust control systems.
-
Durability & uptime: High-quality materials and design reduce maintenance downtime, prolong life, and ensure steady operation.
What types of coking equipment exist (and what do they do)?
Examples include:
-
By-product coke ovens
-
Non-recovery (heat recovery) coke ovens
-
Fluidized bed coking units
-
Delayed coking (in petroleum refineries, though conceptually related)
Each type addresses different feedstock, scale, byproduct handling, and operational parameters.
Thus, when selecting coking equipment, an industrial buyer must consider feed coal properties, desired throughput, emissions constraints, recovery of byproducts, and integration with downstream processes.
Deep Dive: Coke Guide & Coal Bunker
Coke Guide
Coke Guide, the solid carbon-rich residue from coal carbonization, is a critical input in metallurgical, chemical, and energy applications. Its properties (e.g. strength, porosity, ash, fixed carbon) determine its usefulness in blast furnaces, foundries, gasification, and other systems.
Key points:
-
Porosity & reactivity: Coking creates a porous structure, boosting combustion / reduction behavior.
-
Strength & size: Good coke must resist abrasion and maintain structure under high loads.
-
Gas recovery: The volatile products (coal gas, tar, ammonia, sulfur compounds) are condensed and cleaned for reuse or sale.
-
Integration: Coke often goes into blast furnaces, and gases feed heat systems or chemical plants.
Coal Bunker (its role and design)
A coal bunker is the intermediate storage facility between coal feed systems (crusher / pulverizer / feeder) and the coking equipment. Its design and performance are critical because it buffers fluctuations in feed supply, ensures consistent feed rates, and protects against blockages.
Important design and functional factors:
| Feature | Explanation / Importance |
|---|---|
| Capacity & Volume | Must hold sufficient coal to maintain steady feed during interruptions or maintenance. |
| Feed uniformity | Design to permit uniform flow (avoid bridging, rat-holing) into feeders. |
| Structural strength | Must handle the weight, dynamic loads, and possibly temperature effects. |
| Sealing & inert gas / dust control | Minimizes oxygen ingress, dust emission, and spontaneous combustion risks. |
| Feeding mechanism | Rotary feeders, vibrating feeders, or screws may be used to meter coal into the coking system. |
| Monitoring & sensors | Level sensors, flow sensors, temperature sensors to detect surges, blockages or hotspots. |
The coal bunker acts as the buffer, smoothing upstream changes and protecting the downstream coking process from feed disturbance.
Technical Specifications of Our Coking Equipment
Below is a detailed presentation of our coking equipment’s parameters and features. We break down key modules to show professional depth.
A. Core Equipment Modules & Features
| Module / Component | Parameter / Spec | Typical Value / Range | Purpose / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of ovens / chambers | n | 20 – 100 (can custom) | Determines parallel throughput |
| Chamber dimensions | Width × Height × Depth | e.g. 0.6 m × 2.5 m × 15 m | Tailored to capacity & coal type |
| Heating temperature range | 900 °C to 1,300 °C | Depends on coal type | Pyrolysis / carbonization zone |
| Heating rate | °C/hour | 100 – 300 °C/h | Controls volatile release kinetics |
| Coking cycle time | h | 15 – 30 hours | Time for full carbonization + cooling |
| Cooling method | Water quench / inert gas / dry quenching | Customizable | Affects coke quality & emissions |
| Sealing system | Bell seal, hydraulic / mechanical | — | Prevent oxygen ingress, gas leakage |
| Gas recovery & purification | Volume (Nm³/h), sulfur removal (ppm) | e.g. 5,000 Nm³/h, ≤ 100 ppm SO₂ | Meet environmental norms |
| Ash content tolerance | % | ≤ 10 % (depending on coal) | Coal feed requirement |
| Feed coal size | mm | < 50 mm typically | To ensure uniform heating |
| Throughput per chamber | ton/day | e.g. 200–500 t/d | Varies with design |
| Material & lining | Refractory brick, high-grade alloy | — | Withstand high temperature & corrosion |
| Control system | PLC / DCS with SCADA | — | Automation, alarms, data logging |
| Maintenance interval | months | e.g. 12–24 months | For refractory, seals, mechanical parts |
B. Example: Sample Specification for a Mid-Scale Unit
Here is an example configuration:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Total number of chambers | 30 |
| Chamber size (W × H × D) | 0.6 m × 2.5 m × 12 m |
| Cycle time | 24 hours |
| Heating temperature | up to 1,200 °C |
| Throughput per chamber | ~ 300 t/day |
| Total throughput | ~ 9,000 t/day |
| Cooling method | Dry quenching with inert gas |
| Gas recovery | 8,000 Nm³/h, ≤ 80 ppm SO₂ |
| Control system | DCS with remote monitoring |
| Refractory life expectancy | > 2 years under design conditions |
| Coal feed size | 0 – 40 mm |
| Max ash tolerance | 8 % |
C. Integration & Supporting Systems
-
Coal preparation & crushing: Ensure feed coal is in acceptable size.
-
Gas handling & purification: Systems for tar removal, sulfur scrubbing, dust separation.
-
Heat recovery & reuse: Flue gas heat exchangers, steam generation systems.
-
Emission controls: Dust catchers, scrubbers, VOC abatement.
-
Instrumentation & monitoring: Temperature, pressure, gas composition, flow, level sensors.
-
Safety systems: Overpressure relief, inert gas purging, emergency shutdown.
These specifications are customizable — we design per site, coal type, environmental limits, and desired throughput.
Common Questions & Answers about Coking Equipment (FAQ)
Q: What coal properties are critical for good coking performance?
A: The key coal properties include volatile content, ash content, sulfur content, moisture, and size distribution. Low ash, moderate volatile matter, low sulfur, and controlled size are best. These determine coke quality, emissions, and thermal dynamics.
Q: How long is the typical operational lifetime of a coking equipment system?
A: With proper maintenance, refractory renewal, parts replacement, and operation within design parameters, a coking system can serve reliably for 20+ years. Key wear parts (seals, refractory) may require periodic servicing.
Q: How is emission control handled in modern coking plants?
A: Emissions are controlled via gas recovery (capture of volatile gases), tar / ammonia / sulfur scrubbing, dust filters, and inert gas sealing to prevent oxygen ingress. Compliance with local environmental regulations is integrated in the design.
Recent Industry News in Question Form & Summary / Contact
What recent trends or news are influencing the coking equipment sector?
-
Why are steel and energy demands pushing coking plant upgrades?
As global demand for steel and energy intensifies, operators are seeking more efficient, lower-emission coking systems to reduce cost and comply with stricter environmental standards. -
How is carbon regulation affecting coking plants?
Emission caps and carbon pricing in many jurisdictions force coking plant operators to invest in carbon capture, VOC control, and energy recovery systems. -
What innovations are emerging in coking equipment design?
New materials (high-temperature ceramics, advanced alloys), improved control systems (AI/ML predictive maintenance), and modular units for flexible scale are gaining traction.
These news items, framed as questions, align with commonly searched informational queries in industrial equipment and manufacturing sectors.
Our coking equipment offerings are engineered to meet rigorous industrial demands, blending high throughput, emissions control, long lifespan, and flexible customization. Whether your focus is metallurgical coke production, chemical gas recovery, or integrated power generation, we deliver systems built for performance.
We proudly deliver under our Lano, built on decades of engineering and industry trust. For system design, pricing, consultation, or site integration, contact us — we’ll help you design the optimal coking solution tailored to your needs.